What is the Herpes Zoster?
Herpes zoster is caused by the virus Varicella zoster. This name is due to the fact that the virus is the causative agent of two different diseases in clinical manifestations: chicken pox and shingles. The Varicella zoster virus is characterized by neurodermatotropy.
Shingles is a viral disease, which is characterized by damage to the nervous system, mucous membranes of the mouth and skin. It is considered as a re-infection against the background of a decrease in immunity, which has developed as a result of the organism’s contact with the virus in the past. It is believed that the disease occurs as a result of the activation of the virus, which is in a latent state in the nerve ganglia. Most often, shingles occur in the spring and autumn periods. Mostly people are sick at the age of 40-70 years, and men are somewhat more likely than women. In older patients, the disease is more severe and is often complicated by postherpetic neuralgia.
Causes of Herpes Zoster
Tinea in most cases occurs against the background of a weakening of the defenses of the body as a result of the transferred pneumonia, blood diseases, neoplasms and other immunocompromised diseases. As a rule, after the disease, persistent immunity remains. However, in persons suffering from severe chronic diseases (oncological, blood diseases), relapses are possible. Infection is transmitted by contact and airborne pathways.
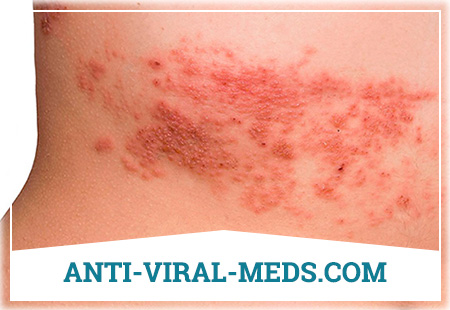
Herpes zoster is characterized by fever, pains of a neuralgic nature and erythematous vesicular vesicles on the skin and mucous membrane along the course of the affected peripheral nerves. Ganglia of some cranial and intervertebral nerves suffer, more often on the one hand. When the first and third branches of the trigeminal nerve are damaged, as well as the trigeminal nerve node (herpetic ganglionitis), rashes of vesicles occur on the mucous membrane of the mouth. Simultaneously, the elements of lesion arise in the area of innervation and on the skin. Localization of the process only on the mucous membrane of the mouth is rare.
In the elderly, often against a background of common severe diseases, cytostatic, corticosteroid therapy develops generalized shingles. It is characterized by a severe course with pronounced intoxication and generalization of bladder rashes, similar to a rash with chicken pox. The meninges and lungs can also be affected, which often leads to death.
Symptoms of Herpes Zoster
In typical cases, the disease begins with pain of varying intensity in the place of future localization of the rash. The nature of pain varies from slightly pronounced pain sensations, paresthesia to painful, burning, cutting, paroxysmal neuralgic pain along the course of affected nerves. Pain is aggravated by stimuli. At the same time, chills, malaise, headache; body temperature rises to 38-39 ° C. The general condition of patients does not always suffer. After 1-5 days after the onset of pain in the affected area, swelling and skin hyperemia develop, against the background of which there are grouped vesicles 1-5 mm in diameter filled with transparent exudate. Simultaneously with the lesion of the skin on the hyperemic mucous membrane of the mouth, there are also multiple vesicles located along the course of the affected nerve. In the oral cavity, the vesicles rapidly open, forming painful single or discharge erosions with scalloped edges, covered with fibrinous coating. Vesicles on the skin are scraped and covered with crusts or, as a result of injury, they are opened with the formation of erosion.
The localization of lesions can be different. Most often, rashes of the blisters are observed on the skin and mucous membrane along the branches of the trigeminal nerve, in the zone of intercostal nerves, on the limbs.
After the epithelization of erosion on the mucous membrane of the mouth and the loss of crusts on the skin, the process ends, leaving a temporary pigmentation. The total duration of the disease is 2-3 weeks. The prognosis is usually favorable, but complications in the form of postherpetic neuralgia, hyperesthesia and hyperpathy, which last for several months or years, are possible in elderly people, as well as in those suffering from severe diseases accompanied by a sharp decrease in immunity (leukemia, oncological diseases). More often, similar phenomena are observed in the elderly, and the older the patient, the higher the probability of postherpetic complications.
Diagnosis of Herpes Zoster
Herpes zoster should be differentiated from:
- acute herpetic stomatitis;
- pemphigus;
- pemphigoid;
- allergic stomatitis;
- when skin is affected – from erysipelas.
Important importance in the diagnosis of herpes zoster are unilateral lesions, no relapse, expressed by a pain symptom, localization of vesicles strictly in the zone innervated by the affected nerve. For the final diagnosis, the following additional methods of investigation are used: general clinical analysis of the blood, virologic (virus isolation from fresh vesicles, blood, cerebrospinal fluid or rinsing from the pharynx), cytological.
Treatment of Herpes Zoster
The main objectives of treatment in herpes zoster are the effect on the causative agent of the disease, the removal of the pain symptom, the normalization of the trophism of the nerve trunks, the prevention of postherpetic neuralgia.
Apply antiviral drugs, metisazon (0.6 g 2 times a day after meals for 6 days); bonafaton (0.1 g 3-5 times a day, three 5-day cycles with 1-2-day breaks); Acyclovir (0.8 g 5 times a day for 5 days). Effective use of deoxyribonuclease. The drug is administered intramuscularly at a dose of 25 mg every 4 hours or 50 mg 2-3 times a day for 7-10 days. There comes a quick stopping process. Treatment with deoxyribonuclease also reduces the likelihood of postherpetic neuralgia.
Local treatment consists in using antiviral drugs (tebrofen, florenal, gossypol, megosin, oxolin, interferon) from the first days of the disease. During the resolution of vesicular rash, keratoplastic agents are shown: rose hips, sea buckthorn, vitamin A, carotolin, “Actovegin” ointment, etc.
Effective from the first days of the disease, laser therapy (helium neon, infrared lasers), UFLuchi.
The pathogenetic basis of the pain symptom and herpetic neuralgia with shingles is the developing puffiness of the nerve trunks and their infringement in narrow bone spaces. To eliminate edema and normalize microcirculatory disorders, dehydration therapy is prescribed: salicylates (acetylsalicylic acid, sodium salicylate 0.5 g 1-3 times a day); 40% glucose solution; Diacarb (0,125-0,25 g 2 times a day in the morning and in the evening). Timely implementation of dehydration therapy quickly enough (already in the first day) relieves acute pain syndrome, promotes rapid relief of the inflammatory process.
To relieve the pain symptom prescribe analgesics, conduct novocain blockade, electrophoresis of novocaine along the affected nerve.
Symptoms of sympathy are stopped by ganglioblokatory: gangleron – pi 1 ml intramuscularly, for a course of 6-8 injections; pachycarpine – 0.05 g 3 times a day.
Correction of microcirculatory disorders appoint quarantil at 0,025-0,05 g 3 times a day for 5-7 days.
The increase in the body’s defenses and its resistance is achieved by the appointment of vitamins: B, (1-2 ml of a 6% solution intramuscularly, for up to 15 injections), B12 (in increasing doses of 200-500 μg per day) intramuscularly, with an improvement in the condition of 100 μg in day, within 2 weeks, ascorbic acid – 0.3-0.5 g per day. Apply also larifan – inducer of interferons – 10 mg subcutaneously once a day for 2 days followed by an interval of 3-4 days. The course of the drug should not exceed 2 weeks. Use adaptogens (preparations of ginseng, eleutherococcus, aralia Manchurian).